What is a variable stream? Things to know about variable currents for monitoring systems
Today, electricity is everywhere around us, present in most homes. But did you know, the current in the system is often very large and cannot be fed directly into measuring devices or other instruments. Therefore, current transformers were born to solve this problem. So what is a current transformer and what role does it play? This is a device that helps convert large currents into smaller currents, suitable for measuring and protecting other devices.
Contents
What is a current transformer?
Current transformer, also known as current transformer (symbol CT), is an important device in the electrical system, helping to change current according to usage needs. Specifically, it can change current from high to low, from low to high, or convert from AC to DC.

Simply put, a current transformer acts as a device that indirectly measures the current passing through the supply or wire to the load. Thanks to that, it supports monitoring and controlling electric current more effectively.
Not only stopping at measurement, current transformers are also responsible for transmitting signals to mechanical meters to display parameters, or send data to the control center, helping the electrical system operate safely and stably. more stable and easier to manage.
Structure and operation of current transformers

1. Structure of current transformer
A current transformer is a device used to transmit current to other devices in the system. It is designed with many turns of wire wrapped around an iron core frame. This simple structure helps the current transformer operate effectively and stably in many environments.
Normally, a basic current transformer will include main components such as:
- Primary Current: Primary current.
- Secondary Winding: Secondary winding.
- Hollow Core: Hollow core.
- Ammeter: Current meter.
2. Operating principle of current transformer
Current transformers operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When an alternating current flows through the primary coil, the magnetic field created induces a current in the secondary coil. This generated current will depend on the number of turns of wire: the more turns of wire, the greater the current generated, and vice versa.
Current transformers operate in two main modes:
- Short circuit mode:
In this mode, the current multiple – that is, the ratio between the primary short-circuit current and the rated current – needs to be kept at an optimal level to ensure the error does not exceed 10%. This error depends on the secondary current or load, which is very important for protection circuits.
- Open circuit mode of secondary current:
To avoid the danger of open secondary circuits, current transformers are often designed with air gaps (also called linear current transformers). This design helps reduce the risk of magnetic saturation, avoiding the appearance of large induction voltages that can be dangerous for equipment or users.
In addition, the current transformer ratio can be adjusted by changing the number of turns in the primary or secondary coil, because the current is inversely proportional to the number of turns.
The role of current transformers in the monitoring system
In modern life, electricity plays an important role and is widely used. Therefore, current transformers are used in many devices such as electricity meters, wattmeters, or protective relays.
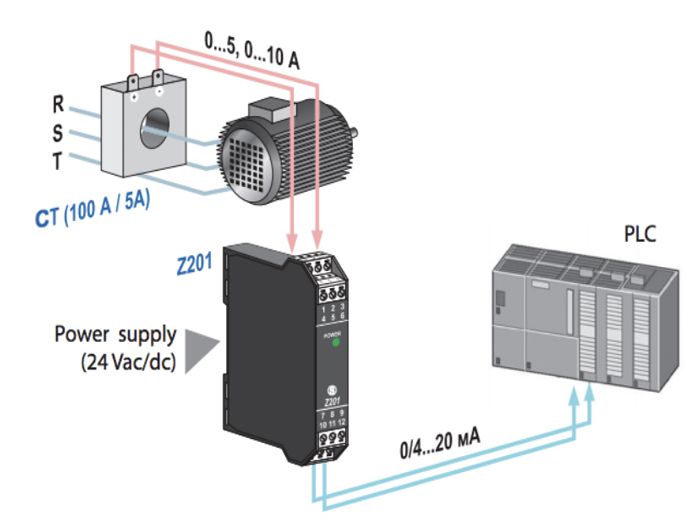
One of the main roles of a current transformer is to provide standard secondary current. This ensures that even if the current reaches its highest level, it is still within the allowable limits of measuring devices such as ammeters. Thanks to that, the system operates safely and stably, while helping users easily monitor and control the electricity flow accurately.